Pattern: Prioritization¶
Motivation¶
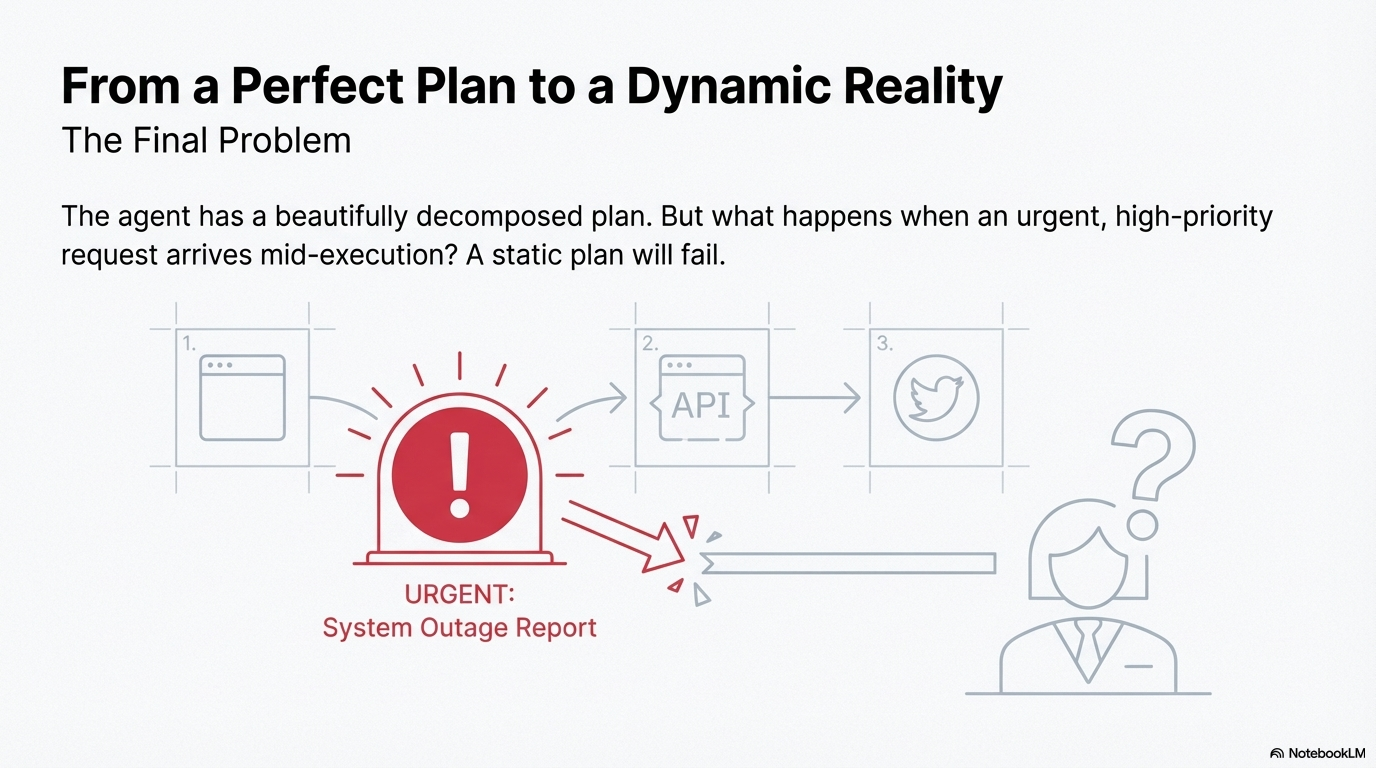
Facing a long to-do list, you assess what's urgent, what's important, and what depends on other tasks. You might tackle urgent deadlines first, then important but less urgent tasks, while considering what blocks other work. Doctors triage patients by severity. Project managers prioritize features by impact. Prioritization in agents mirrors this: evaluating tasks against criteria like significance, urgency, and dependencies to determine the optimal order of execution.
Pattern Overview¶
Problem¶
In complex, dynamic environments, agents frequently encounter numerous potential actions, conflicting goals, and limited resources. Without a defined process for determining the subsequent action, agents may experience reduced efficiency, operational delays, or failures to achieve key objectives. Agentic systems must autonomously manage multiple, often conflicting, tasks or goals under resource constraints to operate effectively, but lack a mechanism to assess and rank tasks based on their significance, urgency, dependencies, and established criteria.
Solution¶
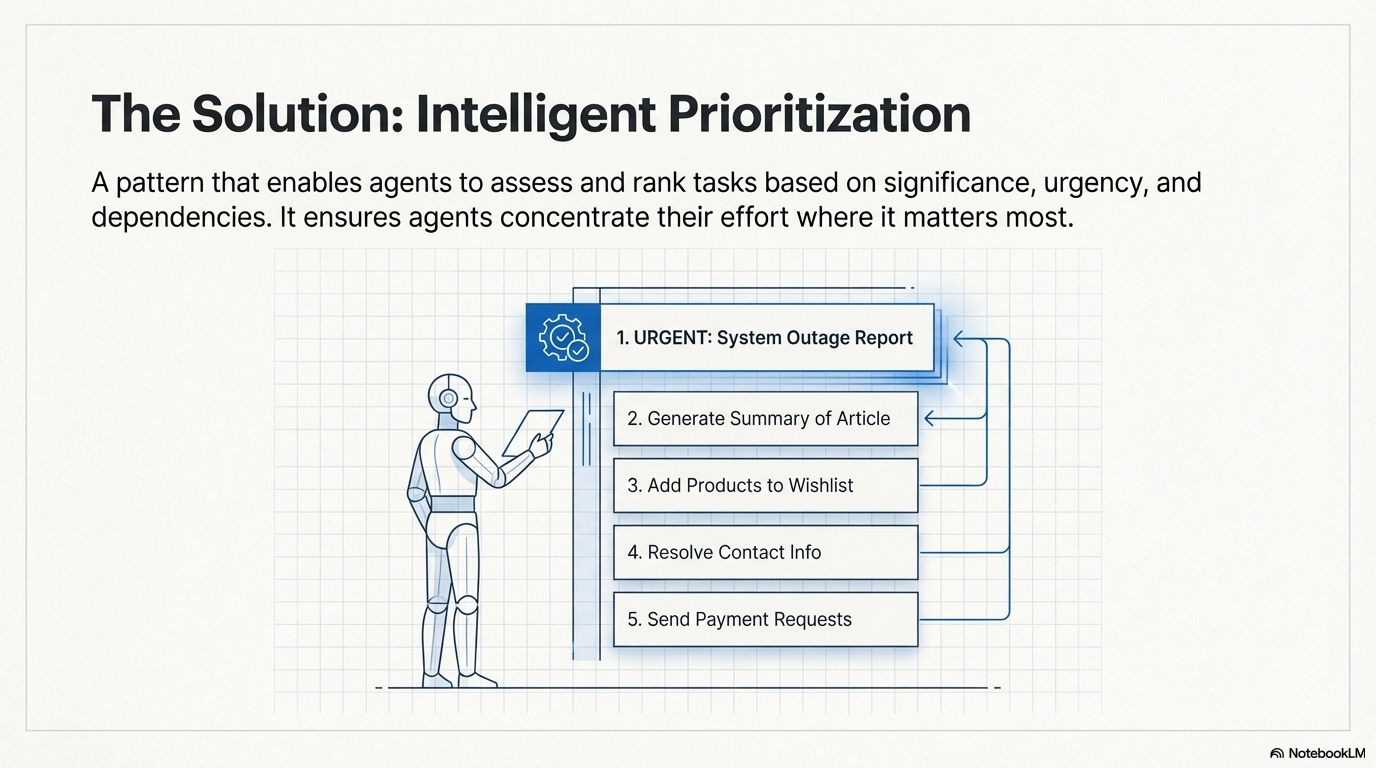
Prioritization is a pattern that enables agents to assess and rank tasks, objectives, or actions based on their significance, urgency, dependencies, and established criteria. This ensures agents concentrate efforts on the most critical tasks, resulting in enhanced effectiveness and goal alignment. The fundamental aspects involve several elements: criteria definition (establishing rules or metrics for task evaluation, including urgency, importance, dependencies, resource availability, cost/benefit analysis, and user preferences), task evaluation (assessing each potential task against these defined criteria, utilizing methods ranging from simple rules to complex scoring or reasoning by LLMs), scheduling or selection logic (the algorithm that, based on the evaluations, selects the optimal next action or task sequence), and dynamic re-prioritization (allowing the agent to modify priorities as circumstances change).
This pattern addresses the challenge by enabling informed decision-making when addressing multiple demands, prioritizing vital or urgent activities over less critical ones. The approach ensures that agents can operate effectively in dynamic environments where tasks, goals, and resource availability change over time.
Key Concepts¶
- Criteria Definition: Establish rules or metrics for task evaluation (urgency, importance, dependencies, resource availability, cost/benefit, user preferences).
- Task Evaluation: Assess each potential task against defined criteria using methods from simple rules to complex LLM-based reasoning.
- Scheduling Logic: Algorithm that selects the optimal next action or task sequence based on evaluations, potentially utilizing queues or planning components.
- Dynamic Re-prioritization: Modify priorities as circumstances change (new critical events, approaching deadlines), ensuring adaptability and responsiveness.
- Multi-Level Prioritization: Prioritization can occur at various levels—selecting overarching objectives (high-level goal prioritization), ordering steps within a plan (sub-task prioritization), or choosing the next immediate action (action selection).
How It Works¶
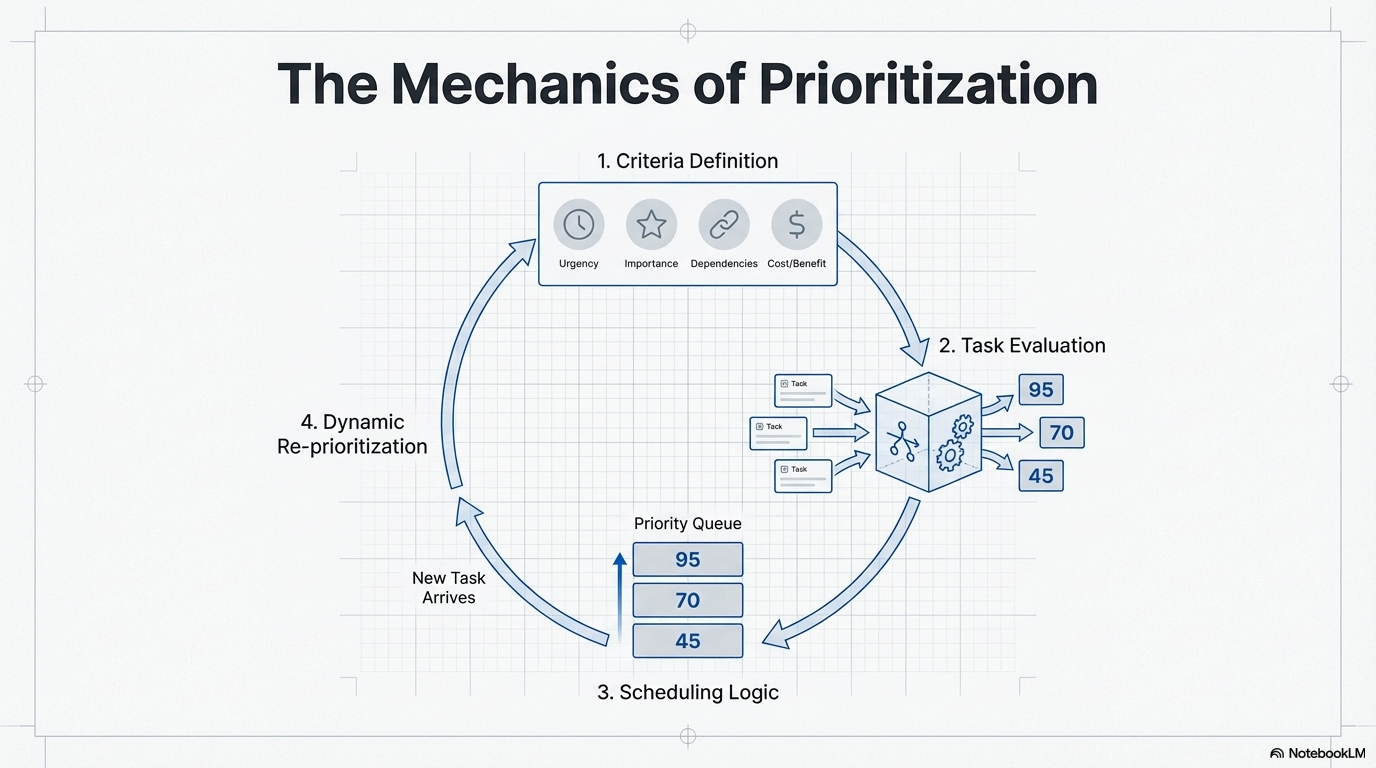
Prioritization operates through a systematic process. First, the agent defines evaluation criteria relevant to its domain and objectives. These criteria might include urgency (time sensitivity), importance (impact on primary objective), dependencies (prerequisites for other tasks), resource availability (readiness of necessary tools or information), cost/benefit analysis (effort versus expected outcome), and user preferences for personalized agents.
Second, the agent evaluates each potential task against these criteria. This evaluation can be rule-based (simple if-else logic), scoring-based (assigning numerical scores to each criterion and aggregating), or LLM-based (using language models to reason about task priority).
Third, based on the evaluations, a scheduling algorithm selects the optimal next action. This might involve sorting tasks by priority score, using a priority queue, or integrating with a planning component that considers task dependencies and resource constraints.
Finally, the system implements dynamic re-prioritization, continuously monitoring the environment and adjusting priorities when new information arrives, deadlines approach, or circumstances change.
When to Use This Pattern¶
✅ Use this pattern when:¶
- Multiple competing tasks: Agents face numerous potential actions with limited resources to execute them all.
- Conflicting goals: Multiple objectives exist that cannot all be pursued simultaneously.
- Resource constraints: Time, computational resources, or other constraints require selective task execution.
- Dynamic environments: Circumstances change frequently, requiring adaptive prioritization.
- User preferences matter: Personalized agents need to consider user-defined importance and preferences.
- Dependency management: Tasks have dependencies that affect their execution order.
❌ Avoid this pattern when:¶
- Single task execution: Only one task or action is available at a time.
- Fixed sequence: Tasks must be executed in a predetermined, unchangeable order.
- Simple scenarios: The order of task execution is trivial or doesn't impact outcomes.
- Real-time constraints: Extremely low-latency requirements where prioritization overhead is prohibitive.
Decision Guidelines¶
Choose this pattern when the benefits of intelligent task ordering outweigh the added complexity. Consider the prioritization method: rule-based prioritization is fast and deterministic but less flexible; scoring-based prioritization offers good balance but requires careful weight tuning; LLM-based prioritization is most flexible but adds latency and cost. The choice depends on your accuracy requirements, latency constraints, and the complexity of the prioritization decision.
Practical Applications & Use Cases¶
Prioritization is essential for building efficient, goal-aligned agentic systems that can manage complexity and resource constraints. Common applications include task management, resource allocation, and dynamic decision-making.
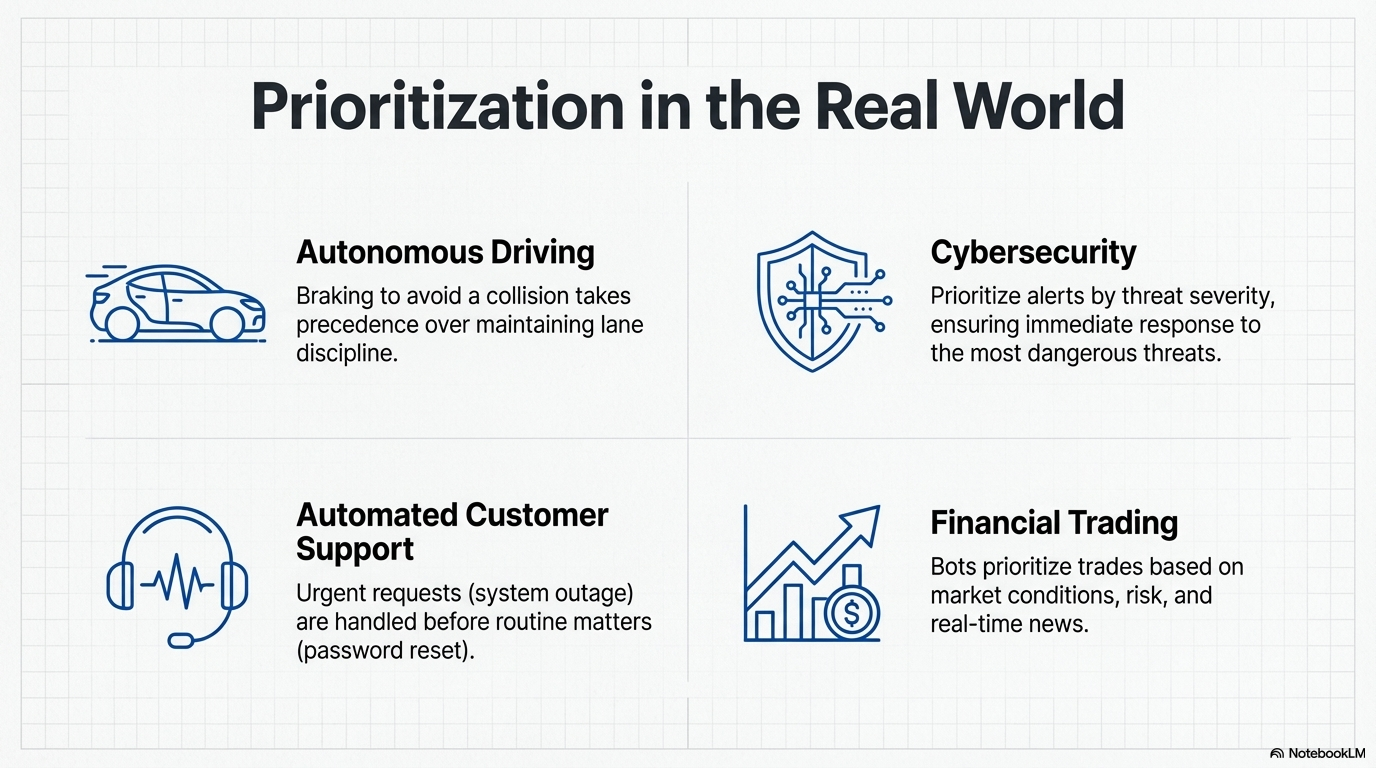
- Automated Customer Support: Agents prioritize urgent requests (like system outage reports) over routine matters (such as password resets), and may give preferential treatment to high-value customers.
- Cloud Computing: AI manages and schedules resources by prioritizing allocation to critical applications during peak demand, while relegating less urgent batch jobs to off-peak hours to optimize costs.
- Autonomous Driving Systems: Continuously prioritize actions to ensure safety and efficiency. For example, braking to avoid a collision takes precedence over maintaining lane discipline or optimizing fuel efficiency.
- Financial Trading: Bots prioritize trades by analyzing factors like market conditions, risk tolerance, profit margins, and real-time news, enabling prompt execution of high-priority transactions.
- Project Management: AI agents prioritize tasks on a project board based on deadlines, dependencies, team availability, and strategic importance.
- Cybersecurity: Agents monitoring network traffic prioritize alerts by assessing threat severity, potential impact, and asset criticality, ensuring immediate responses to the most dangerous threats.
- Personal Assistant AIs: Utilize prioritization to manage daily lives, organizing calendar events, reminders, and notifications according to user-defined importance, upcoming deadlines, and current context.
Implementation¶
Prerequisites:
Basic Example
from typing import List, Dict
from enum import Enum
class Priority(Enum):
P0 = 0 # Critical/Urgent
P1 = 1 # High
P2 = 2 # Medium
P3 = 3 # Low
class Task:
def __init__(self, id: str, description: str, urgency: int = 0,
importance: int = 0, deadline: float = None):
self.id = id
self.description = description
self.urgency = urgency # 0-10 scale
self.importance = importance # 0-10 scale
self.deadline = deadline # Unix timestamp
self.priority_score = self._calculate_priority()
def _calculate_priority(self) -> float:
"""Calculate priority score based on urgency and importance."""
# Weighted combination
base_score = (self.urgency * 0.6) + (self.importance * 0.4)
# Boost for approaching deadlines
if self.deadline:
import time
time_until_deadline = self.deadline - time.time()
if time_until_deadline < 3600: # Less than 1 hour
base_score += 5.0
elif time_until_deadline < 86400: # Less than 1 day
base_score += 2.0
return base_score
def get_priority_level(self) -> Priority:
"""Convert score to priority level."""
if self.priority_score >= 8:
return Priority.P0
elif self.priority_score >= 5:
return Priority.P1
elif self.priority_score >= 2:
return Priority.P2
else:
return Priority.P3
class TaskPrioritizer:
"""Simple task prioritization system."""
def __init__(self):
self.tasks: List[Task] = []
def add_task(self, task: Task):
"""Add a task to the prioritizer."""
self.tasks.append(task)
def get_prioritized_tasks(self) -> List[Task]:
"""Get tasks sorted by priority (highest first)."""
return sorted(self.tasks, key=lambda t: t.priority_score, reverse=True)
def get_next_task(self) -> Task:
"""Get the highest priority task."""
prioritized = self.get_prioritized_tasks()
return prioritized[0] if prioritized else None
# Example usage
prioritizer = TaskPrioritizer()
# Add tasks with different priorities
prioritizer.add_task(Task("T1", "Fix critical security bug", urgency=10, importance=10))
prioritizer.add_task(Task("T2", "Update documentation", urgency=2, importance=3))
prioritizer.add_task(Task("T3", "Review pull request", urgency=5, importance=4))
# Get prioritized list
for task in prioritizer.get_prioritized_tasks():
print(f"{task.id}: {task.description} - Priority: {task.get_priority_level().name}")
# Get next task to work on
next_task = prioritizer.get_next_task()
print(f"\nNext task: {next_task.description}")
Explanation: This basic example demonstrates a simple prioritization system that calculates priority scores based on urgency and importance, with additional boosts for approaching deadlines. Tasks are sorted by their priority scores, and the system can return the highest priority task for execution.
Advanced Example: LLM-Based Prioritization
import os
from typing import List, Optional, Dict
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.tools import Tool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_react_agent
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
load_dotenv()
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.5, model="gpt-4o-mini")
class Task(BaseModel):
"""Represents a single task in the system."""
id: str
description: str
priority: Optional[str] = None # P0, P1, P2
assigned_to: Optional[str] = None
class TaskManager:
"""In-memory task manager."""
def __init__(self):
self.tasks: Dict[str, Task] = {}
self.next_task_id = 1
def create_task(self, description: str) -> Task:
"""Creates and stores a new task."""
task_id = f"TASK-{self.next_task_id:03d}"
new_task = Task(id=task_id, description=description)
self.tasks[task_id] = new_task
self.next_task_id += 1
return new_task
def update_task(self, task_id: str, **kwargs) -> Optional[Task]:
"""Updates a task."""
task = self.tasks.get(task_id)
if task:
update_data = {k: v for k, v in kwargs.items() if v is not None}
updated_task = task.model_copy(update=update_data)
self.tasks[task_id] = updated_task
return updated_task
return None
def list_all_tasks(self) -> str:
"""Lists all tasks currently in the system."""
if not self.tasks:
return "No tasks in the system."
task_strings = []
for task in self.tasks.values():
task_strings.append(
f"ID: {task.id}, Desc: '{task.description}', "
f"Priority: {task.priority or 'N/A'}, "
f"Assigned To: {task.assigned_to or 'N/A'}"
)
return "Current Tasks:\n" + "\n".join(task_strings)
task_manager = TaskManager()
# Tools for the Project Manager Agent
class CreateTaskArgs(BaseModel):
description: str = Field(description="A detailed description of the task.")
class PriorityArgs(BaseModel):
task_id: str = Field(description="The ID of the task to update, e.g., 'TASK-001'.")
priority: str = Field(description="The priority to set. Must be one of: 'P0', 'P1', 'P2'.")
def create_new_task_tool(description: str) -> str:
"""Creates a new project task with the given description."""
task = task_manager.create_task(description)
return f"Created task {task.id}: '{task.description}'."
def assign_priority_to_task_tool(task_id: str, priority: str) -> str:
"""Assigns a priority (P0, P1, P2) to a given task ID."""
if priority not in ["P0", "P1", "P2"]:
return "Invalid priority. Must be P0, P1, or P2."
task = task_manager.update_task(task_id, priority=priority)
return f"Assigned priority {priority} to task {task.id}." if task else f"Task {task_id} not found."
pm_tools = [
Tool(
name="create_new_task",
func=create_new_task_tool,
description="Use this first to create a new task and get its ID.",
args_schema=CreateTaskArgs
),
Tool(
name="assign_priority_to_task",
func=assign_priority_to_task_tool,
description="Use this to assign a priority to a task after it has been created.",
args_schema=PriorityArgs
),
Tool(
name="list_all_tasks",
func=task_manager.list_all_tasks,
description="Use this to list all current tasks and their status."
),
]
# Project Manager Agent
pm_prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """You are a focused Project Manager LLM agent. Your goal is to manage project tasks efficiently.
When you receive a new task request, follow these steps:
1. First, create the task with the given description using the `create_new_task` tool.
2. Next, analyze the user's request to determine priority:
- If urgent/critical/ASAP mentioned → P0
- If important but not urgent → P1
- Otherwise → P2
3. Assign the priority using `assign_priority_to_task`.
4. Use `list_all_tasks` to show the final state.
Priority levels: P0 (highest), P1 (medium), P2 (lowest)
"""),
("placeholder", "{chat_history}"),
("human", "{input}"),
("placeholder", "{agent_scratchpad}")
])
pm_agent = create_react_agent(llm, pm_tools, pm_prompt_template)
pm_agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=pm_agent,
tools=pm_tools,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
memory=ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history", return_messages=True)
)
# Example usage
result = pm_agent_executor.invoke({
"input": "Create a task to implement a new login system. It's urgent and critical."
})
Explanation: This advanced example demonstrates LLM-based prioritization where an agent analyzes task descriptions and automatically assigns priorities based on urgency and importance cues. The agent uses tools to create tasks, assign priorities, and manage the task list, making intelligent prioritization decisions based on natural language input.
Key Takeaways¶
- Core Concept: Prioritization enables agents to intelligently rank and select tasks, ensuring efficient resource utilization and goal alignment.
- Best Practice: Combine multiple criteria (urgency, importance, dependencies) rather than relying on a single factor for robust prioritization.
- Common Pitfall: Over-prioritizing can lead to analysis paralysis; balance thoroughness with decision speed.
- Performance Note: Prioritization adds computational overhead; use efficient algorithms and consider caching for repeated similar decisions.
Related Patterns¶
This pattern works well with: - Planning - Prioritization often informs planning by determining task order - Routing - Prioritization can determine which route or handler to use - Resource-Aware Optimization - Prioritization considers resource constraints when ranking tasks
This pattern is often combined with: - Multi-Agent - Different agents may have different priorities; coordination is needed - Goal Setting and Monitoring - Priorities are often tied to goal achievement - Dynamic Re-prioritization - Priorities change as circumstances evolve
References
- LangChain Agents: https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/agents/
- Task Prioritization in AI Systems: Research on multi-criteria decision making for agents
- Project Management with AI: Best practices for automated task prioritization